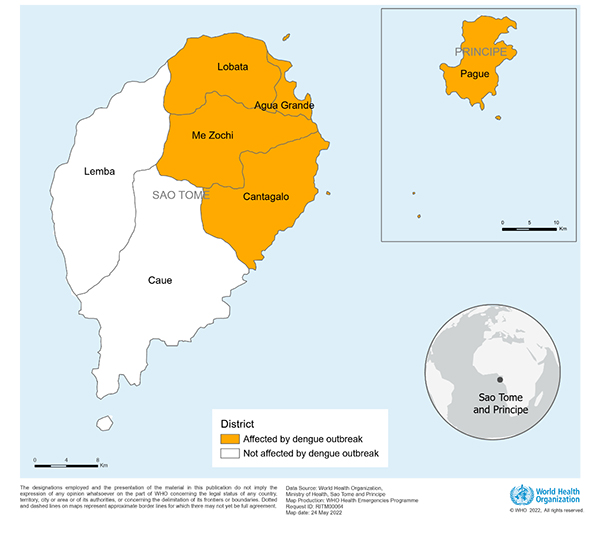
Dengue - Sao Tome and Principe 26 May 2022 Situation at a glance On 13 May 2022, the Ministry of Health (MoH) of São Tomé and Príncipe notified WHO of a dengue outbreak in São Tomé and Príncipe. From 15 April to 17 May, 103 cases of dengue fever and no deaths have been reported. This is the first reported dengue outbreak in the country. Description of the cases From 15 April to 17 May 2022, 103 cases of dengue fever, confirmed by rapid diagnostic test (RDT), and no deaths have been reported from five health districts in São Tomé and Príncipe (figure 1). The majority of cases (90, 87%) were reported from the Água Grande health district followed by Mézochi (7, 7%), Lobata (4, 4%); Cantagalo (1, 1%); and Autonomous Region of Principe (1, 1%) (figure 2). The most commonly affected age groups were: 10-19 years (5.9 cases per 10 000), 30-39 years (7.3 cases per 10 000), 40-49 years (5.1 cases per 10 000) and 50-59 years (6.1 cases per 10 000). The most frequent clinical signs were fever (97, 94%), headache (78, 76%) and myalgia (64, 62%).
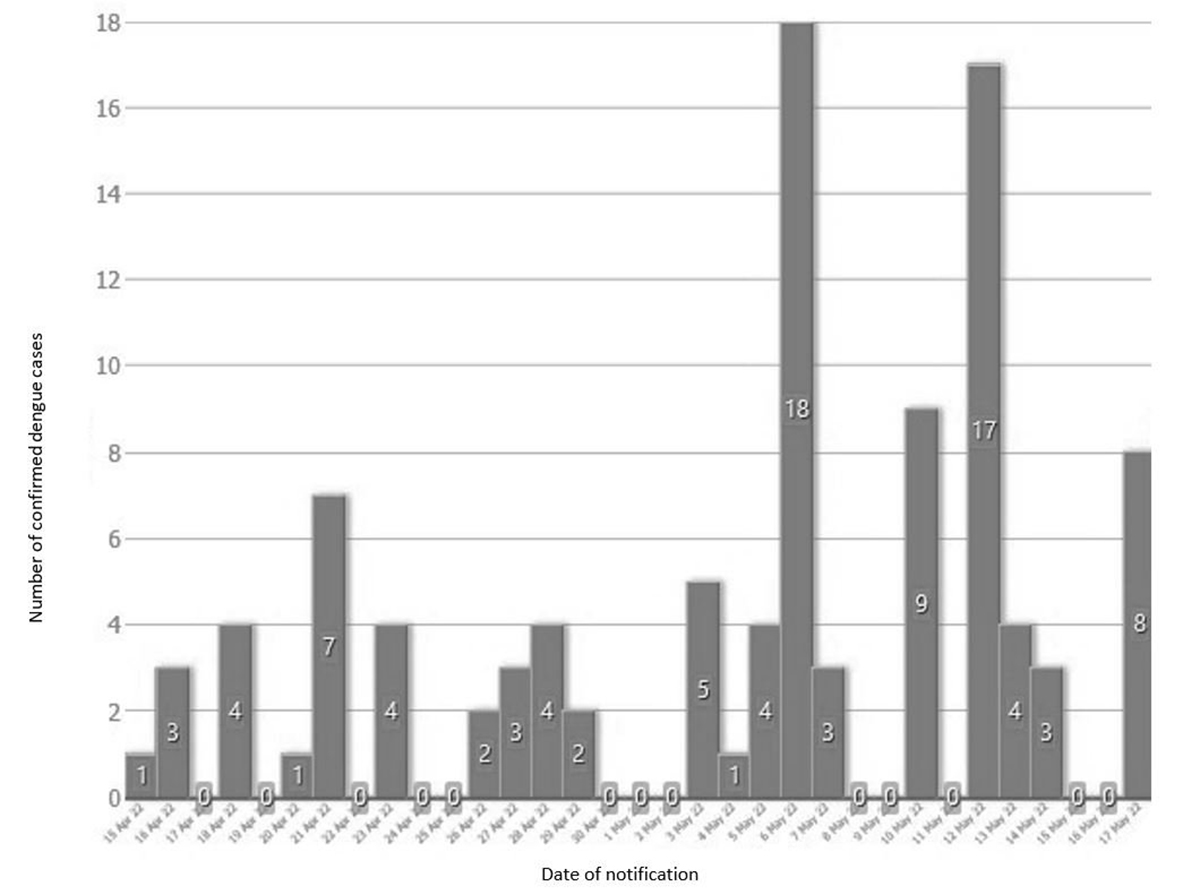
Figure 1. Confirmed cases of dengue in São Tomé and Príncipe by notification date, 15 April to 17 May 2022
A subset of 30 samples confirmed by RDT were sent to an international reference laboratory in Lisbon, Portugal, which were received on 29 April. Further laboratory testing confirmed that the samples were positive for early acute dengue infection, and that the predominant serotype was dengue virus serotype 3 (DENV-3). Preliminary results suggest the possibility of other serotypes present within the batch of samples.
A dengue outbreak alert was initially triggered when a suspected dengue case was reported at a hospital in São Tomé and Príncipe on 11 April. This case, who presented with symptoms suggestive of dengue infection, had travel history and was later diagnosed as having a past dengue infection.
Figure 2. Distribution of confirmed cases of dengue in São Tomé and Príncipe by district, 15 April to 17 May 2022
Epidemiology of the disease
Dengue is a viral infection transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Dengue is found in tropical and sub-tropical climates worldwide, mostly in urban and semi-urban areas. The primary vectors that transmit the disease are Aedes aegypti mosquitoes and, to a lesser extent, Ae. albopictus. The virus responsible for causing dengue, is called dengue virus (DENV). There are four DENV serotypes and it is possible to be infected four times. Many DENV infections produce only mild illness, and over 80% of cases do not exhibit symptoms (asymptomatic). DENV can cause an acute flu-like illness. Occasionally this develops into a potentially lethal complication, called severe dengue.
Public health response
National health authorities have initiated and are undertaking the following measures in response to the outbreak:
Holding weekly meetings between MoH and WHO to discuss technical aspects of the outbreak
Developed, validated and disseminated a dengue response plan
Conducting multidisciplinary epidemiological investigations and active case detections in several health districts
Carrying out entomological investigations to identify breeding sites and conduct fogging and source reduction measures in some affected localities
Publishing a daily bulletin on the disease and regularly sharing with WHO
Organizing deployments of external experts to strengthen laboratory capacity to São Tomé and Príncipe, as well as other potential experts such as for case management, risk communication, entomology and vector control.
WHO risk assessment
The risk at national level is currently assessed as high due to the (i) presence of the mosquito vector Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus; (ii) favourable environment for mosquito breeding grounds following heavy rains and floods since December 2021; (iii) concurrent outbreaks of diarrheal disease, malaria, COVID-19 among other health challenges; and (iv) decreased functionality of sanitation and water management systems in health facilities due to structural damage after heavy flooding. The reported numbers are likely an underestimate because a high proportion of dengue cases are asymptomatic, and there are limitations to the capacity to conduct surveillance and diagnose cases. Clinical management of severe dengue cases is also a challenge. Community awareness in the country is low, and risk communication activities are insufficient.
The overall risk at the regional and global levels are assessed as low. The likelihood of further spread from São Tomé and Príncipe to other countries is unlikely because the country is an island that does not share land borders and it would require the presence of susceptible vectors.
• WHO advice
Case detection
It is important for health facilities to have access to diagnostic tests to detect and/or confirm dengue cases.
Health centres in the outer islands of São Tomé and Príncipe should be made aware of the outbreak and be provided with RDTs for detecting cases.
Vector management Integrated Vector Management (IVM) activities should be enhanced to remove potential breeding sites, reduce vector populations, and minimize individual exposure. This should include both larval and adult vector control strategies, such as environmental management, source reduction and chemical control measures.
Vector control measures should be implemented in households, places of work, schools, and healthcare facilities, among others, to prevent the vector-person contact.
Community-supported source reduction measures should be initiated, as well as vector surveillance.
Personal protective measures
It is recommended to use protective clothing that minimizes skin exposure and apply repellents that can be applied to exposed skin or on clothes. The use of repellents must be in strict accordance with the label instructions.
Window and door screens, and mosquito nets (impregnated or not with insecticide), can be useful to reduce the vector-person contact in closed spaces during the day or night.
Travel and trade
WHO does not recommend any restrictions on travel and trade to São Tomé and Príncipe based on current available information.
Further information
WHO dengue and severe dengue factsheet https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue
WHO African Regional Office, Dengue factsheet https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/dengue
WHO Regional Office for the Americas/Pan American Health Organization, Tool for the diagnosis and care of patients with suspected arboviral diseases https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/33895
Citable reference: World Health Organization (26 May 2022). Disease Outbreak News; Dengue in São Tomé and Príncipe. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2022-DON387
Post time: Aug-26-2022